DNA
The genetic material in all living things is a molecule called DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). Stored in this molecule is information in the form of genes which are used to create proteins. Different genes give instructions on how to make different proteins.
DNA is made from three components
- Sugar (deoxyribose)
- Phosphate
- Bases
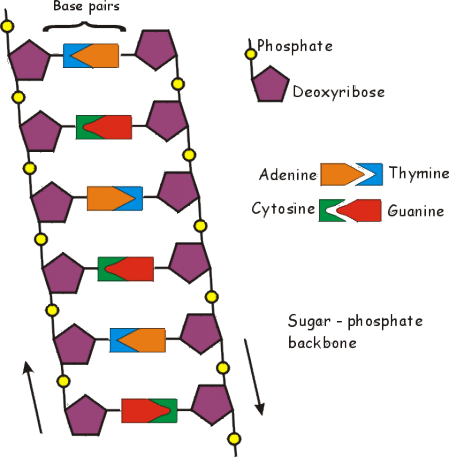
The sugar and phosphate are joined in a chain to form what is known as a sugar-phosphate backbone. Attached to the sugar is a base. There are four different bases in DNA and are adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C) and guanine (G). Two strands of DNA wrap around one another is a double-helix. The bases pair up in a specific way. A always links to T and C always links to G. It is this pairing of bases which enables DNA to make exact copies of itself during cell division.
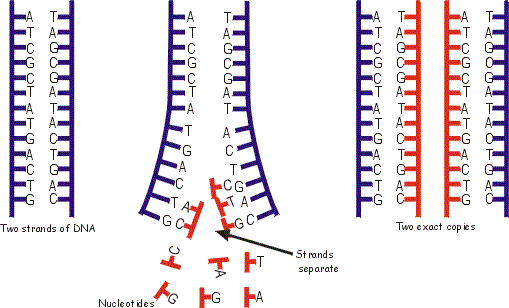
When a cell divides copies of DNA are made. The two strands of DNA separate. Each strand acts as a template for individual nucleotides (a sugar, phosphate group and a base) to bind to. An enzyme known as a ligase stitches the nucleotides into a complete strand. When the process is complete, each original strand of DNA has acted as a template to create two new strands.