Response to Stimulus
A response to a change can be given as :
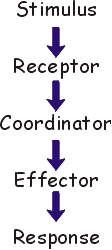
A Stimulus is any change either internal or external which leads to a response. This could be a noise, smell or the changes in blood sugar level.
A Receptor is a specialized cell which can sense the stimulus. There are lots of different types of receptors, some can sense light, while others can sense heat etc.
A Coordinator is a cell or organ which 'decides' what to do. It gives a message to the effector to do something.
The Effector is an organ which responds to the stimulus. This could be a muscle which contracts or an organ like the liver which may perform a complex task like lowering the blood sugar levels after a meal.
The Response is what happens when the organism reacts to the stimulus.
The stimulus could be either external or internal. An example of an external stimulus would be the response of the iris to bright light. Bright light can damage the retina. In this case the light is the stimulus. The receptors are the light sensitive cells of the retina. The brain is the coordinator which decides that the light is too bright and stimulates the effector, in this case the circular muscles of the iris. The response is that the iris contracts making the pupil narrower and so reducing the amount of light which enters the eye. An internal stimulus could be the body's temperature control. The stimulus in this case is the temeprature of the blood. The hypothalamus of the brain is the receptor and the brain is the coordinator. There are a number of effectors in this case. The sweat glands, erector muscles and the blood vessels of the skin are just a few.
