How We Breathe
When we breathe, air is drawn into the lungs so that gaseous exchange can take place. The lungs are unable to draw in air on their own. The chest cavity where the lungs are positioned, is an air tight container.
When we breathe in the diaphragm muscle contracts, pulling the sheet down. The intercostal muscles in between the ribs also contract which pulls the whole ribcage upwards and outwards. These together increase the volume of the chest. Air is drawn into the lungs because the the pressure inside them is lowered as the chest volume is increased.
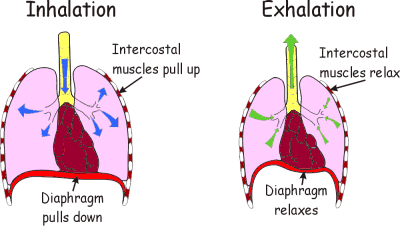
When we breathe out the diaphragm relaxes as does the intercostal muscles.This decrases the volume of the chest, increasing the pressure. This forces air out of the lungs.
So it is the changing volume of the chest which causes air to enter and leave the lungs. The lungs themselves are just like balloons which are inflated and deflated.
