Heartbeat
When the heart beats it takes in blood from the veins and forces it into the arteries. The heart is really two pumps stuck together. Each pump has two chambers. When the right atrium contracts, the same happens to the left-hand side. The same is true when the right ventricle contracts.
The blood must flow through the heart in one direction. Blood enters the atria from the veins and is then forced into the ventricles. The ventricles force the blood into the arteries. There are a number of sphincter muscles and valves that prevent blood flowing the wrong way. The valves are a little like parachutes. When blood flows the wrong way the valves bulge out, blocking the path.
Heartbeat involves three distinct stages:
1) relaxation phase - diastole
2) atria contract - atrial systole
3) ventricles contract - ventricular systole
| Events in Phase | Diagram (only one side shown) |
|---|---|
| DIASTOLE 1) The atria and the ventricles relax. 2) The semi-lunar valves close, preventing back flow into the ventricles. 3) The elastic walls of the aorta & pulmonary artery contract, forcing blood towards the body & the lungs. 4) Blood from the veins flows into the atria, which begin to fill. Deoxygenated blood enters the right atrium, and oxygenated blood flows into the left atrium. |
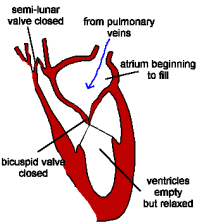
|
| ATRIAL SYSTOLE 1) The atria contract, forcing blood into the ventricles, which fill. 2) Sphincter (ring) muscles closing off the venae cavae and the pulmonary veins prevents backflow from the atria into the main veins. |
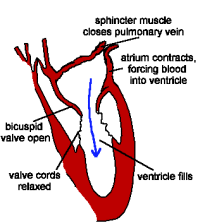
|
| VENTRICULAR SYSTOLE 1) The ventricles contract, forcing blood into the aorta & pulmonary artery. 2) The main heart valves (tricuspid & bicuspid) are forced shut, so preventing backflow into the atria. This happens because the pressure of blood in the ventricles is higher than the pressure in the atria. The valve cords prevent the valve being pushed back too far. 3) The walls of the aorta & pulmonary artery expand. |
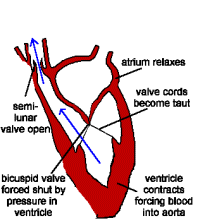 |
The table below shows a summary of what happens in heart beat.
| Phase | Atria | Ventricles | Cuspid valves | Semi-lunar valves |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diastole | Relaxed | Relaxed | Closed | Closed |
| Atrial systole | Contracting | Relaxed | Open | Closed |
| Ventricular systole | Relaxed | Contracting | Closed | Open |
