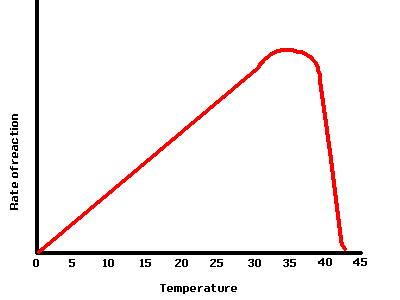
How temperature affects Enzymes
Generally speaking heating up a chemical reaction makes it go quicker. This is because chemicals need energy in order to react, heat them up and a greater proportion of the chemicals have the right amount of energy needed to react. Also the hotter the chemicals are the faster their particles move around. This increases the chances of chemicals colliding and collisions between particles are needed for chemical reactions to take place.
Enzymes though are sensitive to extreme heat. They are very large proteins whose three dimensional shape is vital for their activity. When proteins are heated up too much they vibrate. If the heat gets too intense then the enzymes literally shake themselves out of shape. The enzyme is said to be denatured. Enzymes generally become denatured when heated above 40ºC. The optimum temperature for enzymes to work at is around 37ºC which is why this temperature is body temperature. Temperatures lower than optimum mean the chemical reaction will be slower for the reasons stated above.